
What Is CBG Oil?
If you’re looking for a comprehensive, natural solution to tackle inflammation and its debilitating effects, you’re in the right place. Welcome to the new era

Diabetes is a chronic condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Managing diabetes can be challenging, but adopting a ketogenic (keto) diet may provide some benefits. This guide will explore the keto diet for diabetics, including delicious recipes and alternatives to your favorite treats.
The keto diet is a low-carb, high-fat diet that has been shown to help some diabetics improve their blood sugar control and potentially reduce their dependency on medications.
It can also support weight loss and overall health, which are important factors in managing diabetes.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the ins and outs of the keto diet for diabetics, providing you with the information and tools you need to make an informed decision about whether this lifestyle change is right for you.
From mouthwatering recipes to practical tips on managing blood sugar levels, our goal is to help you enjoy the benefits of the keto diet while maintaining optimal health and well-being.
The ketogenic or “keto” diet is a low-carbohydrate, moderate-protein, and high-fat eating plan that has gained popularity in recent years for its potential weight loss and health benefits.
The primary goal of the keto diet is to shift the body’s metabolism from burning glucose (sugar) as its primary fuel source to burning ketones, which are produced when the body breaks down fats.
This metabolic state is called ketosis, and it can help improve fat burning, stabilize blood sugar levels, and increase satiety, among other benefits.
The keto diet typically involves drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing the consumption of healthy fats and moderate amounts of protein. By doing so, it encourages the body to enter a state of ketosis, in which it relies more heavily on fats for energy.
Carbohydrates are usually limited to approximately 5-10% of total daily caloric intake, with fats accounting for 70-80% and proteins making up the remaining 15-20%.
One of the key advantages of the keto diet for people with diabetes is its potential to improve blood sugar control.
By minimizing the intake of carbohydrates, the diet helps prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar levels and can even lead to a reduction in insulin resistance over time. This can be particularly beneficial for those with type 2 diabetes, as improved insulin sensitivity may lead to a reduced need for diabetes medications.
However, it’s essential to note that the keto diet is not a one-size-fits-all solution and may not be suitable for everyone.
Some individuals with diabetes, particularly those with type 1 diabetes, may experience challenges with the keto diet, such as an increased risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or ketoacidosis (a dangerous build-up of ketones in the blood).
As you explore the keto diet for diabetics, you’ll find that it offers a wide variety of delicious and satisfying foods, making it an enjoyable and sustainable lifestyle choice for those who choose to embark on this dietary journey.
The keto diet has been shown to provide several potential benefits for people with diabetes.
By reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing the consumption of healthy fats and moderate amounts of protein, the keto diet can help improve blood sugar control, weight management, and overall health in some individuals with diabetes.
Some of the primary benefits of the keto diet for diabetics include:
Many individuals with diabetes have reported success in managing their condition with the keto diet, making it a viable option for those seeking an alternative dietary approach to support their diabetes care plan.
Embarking on the keto diet can seem daunting, but with the right guidance, it can be a smooth and rewarding journey. In this section, we’ll break down the process into clear and simple steps that will help you get started with confidence.
Before starting the keto diet, it’s essential to determine your ideal macronutrient ratios.
Typically, the macronutrient breakdown for a keto diet consists of approximately:
Calculate your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) and Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) using the Mifflin-St Jeor equation:
Next, calculate your TDEE by multiplying your BMR by an activity factor based on your daily activity level:
Use your TDEE and the recommended macronutrient breakdown to determine your daily macronutrient requirements, ensuring you have the right balance of carbs, protein, and fat.
Now that you have your macronutrient goals, it’s time to plan your meals.
For your first week, focus on incorporating keto-friendly foods into your diet. It’s essential to have a variety of meal and snack options to keep your diet interesting and satisfying.
Here are 20 meal ideas, along with some snack suggestions, to help you create a diverse and delicious keto meal plan.
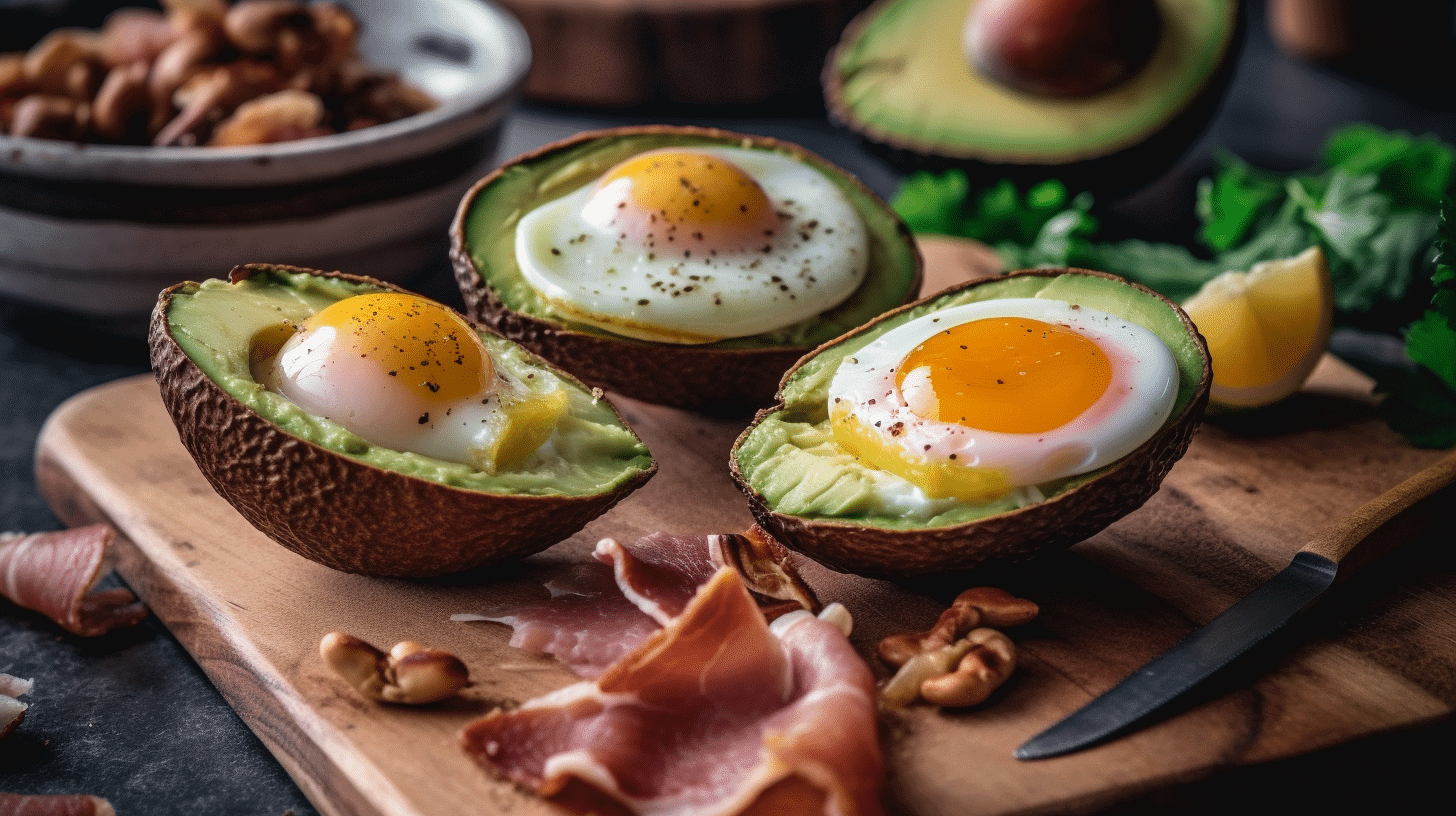
Avocado and egg breakfast bowls with cherry tomatoes and crumbled feta cheese:
Greek salad with cucumber, olives, red onion, and feta, drizzled with olive oil:
Baked salmon with a lemon-dill sauce, served with steamed asparagus:
Keto-friendly taco salad with ground beef, avocado, shredded cheese, and sour cream:
Garlic butter shrimp served over zucchini noodles:
Grilled chicken with a creamy spinach and artichoke sauce:
Cauliflower fried rice with scrambled eggs, diced vegetables, and soy sauce (or use a sugar-free alternative like coconut aminos or tamari):
Creamy mushroom and bacon-stuffed chicken breast with a side of green beans:
Zucchini lasagna with layers of ground beef or turkey, ricotta cheese, and marinara sauce:
Keto-friendly pizza with a cauliflower or almond flour crust, topped with cheese, pepperoni, and your favorite low-carb vegetables:
Egg roll in a bowl with ground pork, cabbage, and Asian-inspired seasonings:
Chicken Caesar salad with romaine lettuce, Parmesan cheese, and a low-carb Caesar dressing:
Low-carb beef and broccoli stir-fry with a sugar-free teriyaki sauce:
Caprese salad with fresh mozzarella, tomatoes, and basil, drizzled with balsamic glaze (look for a sugar-free version)
Spinach and feta-stuffed pork tenderloin with a side of roasted Brussels sprouts
Grilled steak with garlic herb butter and a side of loaded cauliflower mash
Jalapeno popper chicken casserole with cream cheese, shredded cheddar, and bacon
Keto-friendly chili made with ground beef, green peppers, onions, and tomatoes (skip the beans):
Cobb salad with grilled chicken, hard-boiled eggs, avocado, bacon, and blue cheese:
Sausage and vegetable sheet pan dinner with bell peppers, onions, and cherry tomatoes:
For snacks, consider the following keto-friendly options:
With these meal and snack ideas, you can create a meal plan for the week that aligns with your macronutrient goals.
Utilize online recipes, meal planning apps, or consult a nutrition expert to help you create delicious and satisfying keto meals.
To minimize the potential side effects of starting the keto diet, such as the “keto flu,” it’s essential to transition gradually.
This means reducing your carbohydrate intake slowly over several weeks, rather than eliminating them all at once. This approach allows your body to adjust to the change and can help prevent any sudden discomfort. Here’s how to make a gradual transition:
When transitioning to a keto diet, it’s crucial to stay hydrated and maintain electrolyte balance.
The body tends to lose water and electrolytes more rapidly on a low-carb diet, which can lead to dehydration, fatigue, and other symptoms. Follow these tips to ensure proper hydration and electrolyte balance:
As you progress through your keto journey, it’s essential to monitor your progress and make any necessary adjustments.
Regularly check in with yourself to assess how you feel, track your weight loss or health goals, and ensure you’re consuming nutrient-dense foods. If you notice any issues, such as a lack of energy, consider adjusting your macronutrient ratios or increasing your calorie intake.
Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine to support your overall health and weight loss goals.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 70 minutes of high-intensity exercise per week, along with strength training activities on two or more days per week. Choose activities that you enjoy, and consider working with a personal trainer or joining a group fitness class for added motivation and support.
You can break 70 minutes of high-intensity exercise up into just 10 minutes every day!
Maintaining a keto diet doesn’t mean you have to give up all of your favorite foods. With a little creativity and some clever substitutions, you can still enjoy many delicious meals and treats that fit within your low-carb, high-fat lifestyle. Here are some keto-friendly alternatives to your favorite foods:
Traditional pizza crusts are high in carbs, but you can make a keto-friendly pizza by using alternative crusts. Two popular options are cauliflower crust and almond flour crust. Both are low in carbs and offer a satisfying texture that mimics traditional pizza dough. Top your keto pizza with sugar-free tomato sauce, plenty of cheese, and your favorite low-carb toppings, such as pepperoni, mushrooms, and olives.
If you’re missing bread on your keto diet, you can try making your own low-carb bread using ingredients like almond flour, coconut flour, or ground flaxseed. There are numerous keto bread recipes available online, ranging from sandwich bread to bagels and even hamburger buns. You can also purchase pre-made keto bread at some specialty stores or online.
Regular pasta is off-limits on a keto diet, but there are several low-carb pasta alternatives to choose from. Spiralized vegetables, such as zucchini noodles (zoodles) or spaghetti squash, make a great substitute for traditional pasta. You can also try shirataki noodles, which are made from the fiber-rich konjac plant and are virtually carb-free.
To replace rice in your favorite dishes, try cauliflower rice. Simply pulse raw cauliflower florets in a food processor until they reach a rice-like consistency. You can then sauté the cauliflower rice in a bit of oil or butter and season it with your favorite spices. Cauliflower rice works well as a side dish or as a base for stir-fries and other meals.
While potatoes are not keto-friendly, you can substitute them with other low-carb vegetables in many dishes. For example, try using mashed cauliflower as a replacement for mashed potatoes, or make oven-roasted radishes or turnips instead of potato wedges.
Satisfy your sweet tooth with keto chocolate chip cookies made from almond flour or coconut flour. Use a sugar substitute, such as erythritol or stevia, to sweeten the cookies and opt for sugar-free dark chocolate chips or cacao nibs to maintain the classic chocolate chip flavor.
For a low-carb alternative to potato chips, try making your own keto-friendly chips using vegetables like zucchini, kale, or radishes. Slice the vegetables thinly, toss them in oil and seasonings, and bake them in the oven until crispy. Cheese crisps are another great option. Simply place small mounds of shredded cheese on a parchment-lined baking sheet and bake until golden and crispy.
Make your own keto gummy candies using sugar-free gelatin, water, and a low-carb sweetener like erythritol or stevia. Pour the mixture into silicone candy molds and refrigerate until set. You can customize the flavor and color by using different sugar-free flavored gelatins or adding natural food coloring.
Bacon is already keto-friendly, so there’s no need to find an alternative. However, be sure to choose a brand that’s free of added sugars and nitrates. Enjoy bacon on its own, crumbled over salads, or wrapped around your favorite keto-friendly vegetables or proteins.
Chicken wings are a popular keto food, but be careful with the sauces and seasonings. Many commercial wing sauces contain added sugars.
You can enjoy keto ice cream by making your own with heavy cream, unsweetened almond milk, a sugar substitute like erythritol, and flavorings such as vanilla extract or cocoa powder. There are also commercial keto-friendly ice creams available at many grocery stores, but always check the labels for hidden sugars and carbs.
Create keto pancakes using almond flour or coconut flour, eggs, unsweetened almond milk, and a sugar substitute. Add in flavorings like vanilla extract or cinnamon, and top your pancakes with sugar-free syrup, whipped cream, or fresh berries.
Replace traditional taco shells with low-carb alternatives such as lettuce wraps, cheese taco shells, or almond flour tortillas. Fill your keto tacos with your choice of protein, avocado, cheese, sour cream, and salsa for a delicious and satisfying meal.
Instead of high-carb popcorn, try snacking on roasted nuts or seeds, such as almonds, pecans, or pumpkin seeds. Season them with your favorite spices for a tasty and nutritious snack.
Make keto brownies using almond flour or coconut flour, unsweetened cocoa powder, a sugar substitute, and unsweetened chocolate or sugar-free chocolate chips. Enjoy these rich, chocolatey treats without the guilt.
For a low-carb cereal alternative, try making a homemade keto granola using nuts, seeds, unsweetened coconut flakes, and a sugar substitute. You can also find commercial keto-friendly cereals at specialty stores or online.
Swap out traditional french fries for low-carb alternatives like jicama fries, eggplant fries, or zucchini fries. Simply slice your chosen vegetable into fry shapes, toss in oil and seasonings, and bake or air fry until crispy.
Create keto muffins using almond flour or coconut flour, eggs, a sugar substitute, and your choice of flavorings, such as vanilla extract, cocoa powder, or lemon zest. Add in berries, nuts, or sugar-free chocolate chips for extra texture and flavor.
Make your own keto crackers using almond flour, egg, and seasonings. You can also purchase pre-made low-carb crackers at specialty stores or online.
Many store-bought ketchups contain added sugars, so opt for a sugar-free or low-carb ketchup alternative. You can also make your own keto-friendly ketchup using tomato paste, apple cider vinegar, a sugar substitute, and seasonings.
Whip up a keto smoothie using unsweetened almond milk or coconut milk, avocado, spinach, and a sugar substitute. Add in flavorings like vanilla extract, unsweetened cocoa powder, or a few berries for a refreshing and nutritious drink.
Replace traditional lasagna noodles with thinly sliced zucchini, eggplant, or cabbage leaves. Layer your keto lasagna with a sugar-free tomato sauce, ground meat, cheese, and your favorite low-carb vegetables.
Create keto donuts using almond flour or coconut flour, a sugar substitute, and flavorings like vanilla extract or cinnamon. Bake the donuts in a donut pan and top with a sugar-free glaze or frosting.
Make a keto cheesecake with an almond flour crust and a filling made from cream cheese, eggs, a sugar substitute, and vanilla extract. Top your cheesecake with sugar-free whipped cream and fresh berries for an indulgent dessert.
To make keto biscuits, use almond flour, coconut flour, or a combination of both, along with cold butter, eggs, and a leavening agent like baking powder. Add in seasonings such as garlic powder, onion powder, or herbs for a savory twist. Shape the dough into biscuits and bake until golden brown. Enjoy these low-carb biscuits with butter or your favorite keto-friendly spread.
Make your own keto pretzels using almond flour, mozzarella cheese, cream cheese, and a leavening agent. Shape the dough into pretzels and bake until golden brown. Enjoy them plain or with your favorite low-carb dip.
Create keto granola bars using a combination of nuts, seeds, unsweetened coconut flakes, almond flour, a sugar substitute, and a binding agent like melted butter or coconut oil. Press the mixture into a pan, refrigerate until set, and cut into bars for a portable snack.
Use keto bread made from almond flour or coconut flour to create a low-carb grilled cheese sandwich. Fill the sandwich with your choice of cheese and grill until the cheese is melted and the bread is crispy.
For a keto-friendly alternative to oatmeal, try making “noatmeal” using a combination of ground flaxseed, chia seeds, and unsweetened shredded coconut. Cook the mixture in unsweetened almond milk or coconut milk and sweeten with a sugar substitute. Add in your favorite low-carb toppings, such as nuts, seeds, or a small amount of berries.
Many store-bought salad dressings contain added sugars and unhealthy oils. Make your own keto-friendly salad dressings using ingredients like olive oil, vinegar, lemon juice, mustard, herbs, and spices. You can also find sugar-free or low-carb salad dressings at specialty stores or online.
Replace high-carb pasta with low-carb alternatives like cauliflower or shirataki noodles for a keto-friendly mac and cheese. Combine your chosen low-carb “pasta” with a rich cheese sauce made from heavy cream, cream cheese, and your favorite shredded cheeses.
Create keto energy bars using nuts, seeds, almond or coconut flour, a sugar substitute, and a binding agent like nut butter or coconut oil. Press the mixture into a pan, refrigerate until set, and cut into bars for an on-the-go snack.
Make a keto-friendly pudding using heavy cream, unsweetened almond milk, a sugar substitute, and flavorings like vanilla extract or unsweetened cocoa powder. Thicken the pudding with a small amount of xanthan gum or gelatin.
Replace traditional rice with cauliflower rice for a low-carb fried rice dish. Sauté the cauliflower rice with your choice of protein, vegetables, and seasonings for a quick and satisfying meal.
Swap high-carb mashed potatoes for mashed cauliflower by steaming cauliflower florets and then blending them with butter, cream, and seasonings until smooth. This creamy side dish is a great accompaniment to your favorite keto-friendly proteins.
Make keto nachos by using cheese crisps or thinly sliced zucchini as a base instead of high-carb tortilla chips. Top your low-carb “chips” with seasoned ground meat, cheese, sour cream, avocado, and your favorite keto-friendly toppings.
Create keto waffles using almond flour or coconut flour, eggs, unsweetened almond milk, a sugar substitute, and a leavening agent. Cook the waffle batter in a waffle iron and serve with sugar-free syrup, whipped cream, or fresh berries.
Replace high-carb breadcrumbs with low-carb alternatives like crushed pork rinds, almond flour, or grated Parmesan cheese. Use this keto-friendly breading for dishes like chicken tenders, fish sticks, or breaded vegetables.
Rather than consuming sugar-laden soda, opt for keto-friendly alternatives such as sparkling water, sugar-free flavored water, or diet soda made with keto-friendly sweeteners like erythritol or stevia. You can also make your own flavored soda by combining sparkling water with a sugar-free syrup or a few drops of liquid stevia and natural flavor extracts.
For a keto-friendly alternative to high-carb tortilla chips, try using thinly sliced cucumber, celery sticks, or cheese crisps as dippers. Pair them with a low-carb salsa made from fresh tomatoes, onions, cilantro, lime juice, and jalapeños.
Section 2: Intermittent Fasting for Diabetics
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a dietary approach that involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. It has gained considerable popularity in recent years, thanks to its potential health benefits and the flexibility it offers.
Unlike traditional diets that focus primarily on what you eat, intermittent fasting is more concerned with when you eat. By strategically controlling the timing of your meals, you can potentially promote weight loss, improve metabolic health, and even increase longevity.
There are several methods of intermittent fasting, each with its own specific eating and fasting schedule. Some of the most popular approaches include:
It’s essential to understand that intermittent fasting is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and the most effective method will depend on your individual preferences, lifestyle, and health goals. Before starting intermittent fasting, it’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have any pre-existing medical conditions or concerns.
During the fasting periods, it’s crucial to stay hydrated by drinking water, black coffee, or other no-calorie, unsweetened beverages.
It’s also essential to ensure that, during your eating windows, you consume nutrient-dense foods that provide adequate protein, healthy fats, and essential micronutrients. This will help to support overall health and ensure that your body receives the necessary nutrients for proper functioning.
Intermittent fasting offers numerous potential benefits, including:
It’s worth noting that while many people find success with intermittent fasting, it may not be suitable for everyone. Pregnant or breastfeeding women, individuals with a history of eating disorders, and those with certain medical conditions may need to avoid fasting or approach it with caution.
Starting intermittent fasting can seem daunting at first, but by following these steps, you can ease into the process and set yourself up for success.
There are several intermittent fasting methods available, each with its own eating and fasting schedule.
Review the methods described in section 2.1 and select the one that best fits your lifestyle, preferences, and health goals. Keep in mind that you can always adjust your chosen method or switch to another one if needed.
Once you’ve chosen a fasting method, create a consistent eating and fasting schedule that you can maintain over time.
Consistency is key when it comes to intermittent fasting, as it helps your body adapt to the new routine and allows you to experience the full range of potential benefits.
During your eating windows, prioritize nutrient-dense foods that provide adequate protein, healthy fats, and essential micronutrients. This will ensure that your body receives the necessary nutrients for proper functioning and support your overall health.
Some examples of nutrient-dense foods include:
During your fasting periods, it’s crucial to stay hydrated by drinking water, black coffee, or unsweetened tea. These beverages contain no calories and can help suppress appetite and maintain energy levels.
Track your progress by regularly checking in with yourself and noting any changes in your energy levels, mood, and physical health.
If you’re not experiencing the desired results or are struggling with your fasting schedule, consider making adjustments to your chosen method or trying a different approach.
To support your overall health and weight loss goals, incorporate regular physical activity into your routine.
Exercise can enhance the benefits of intermittent fasting and help you achieve your desired results more quickly.
Intermittent fasting can take some time to adjust to, and it’s essential to be patient with yourself during the transition.
Listen to your body’s signals, and if you experience persistent negative side effects, consider making changes to your fasting method or consulting a healthcare professional for guidance.
By following these steps, you can successfully start intermittent fasting and begin to experience the potential benefits of this dietary approach. Remember that consistency, patience, and self-care are essential for success.
Eating out while following a keto diet or intermittent fasting can be challenging, but with some planning and knowledge, you can enjoy a meal at a restaurant while staying on track.
Here are some tips to help you navigate restaurant menus and make informed choices.
Before visiting a restaurant, take some time to research its menu online. This will give you an idea of the available options and help you plan your meal accordingly.
Look for dishes that are low in carbohydrates and high in healthy fats and protein. If nutritional information is available, review it to ensure the meal aligns with your dietary goals.
Don’t be afraid to ask for modifications to dishes to make them keto-friendly or suitable for your intermittent fasting schedule.
For example, you might request to:
Most restaurants are willing to accommodate dietary requests, so don’t hesitate to communicate your needs.
Select appetizers and side dishes that are low in carbs and high in healthy fats and protein.
Some keto-friendly options include:
When choosing a main dish, focus on protein-based options that are grilled, baked, or broiled.
Some examples include:
Some dishes may contain hidden carbs in the form of sauces, dressings, or breading.
Be cautious of dishes that include:
If you’re following an intermittent fasting schedule, plan your eating window around the time you’ll be dining out.
This will allow you to enjoy a meal with friends or family without breaking your fast.
If you’d like to enjoy a dessert or treat while dining out, look for low-carb options like:
Remember that moderation is key, and it’s okay to indulge occasionally as long as you’re mindful of your overall dietary goals.
By following these steps and being proactive in your meal planning, you can successfully navigate restaurant menus and enjoy dining out while staying on track with your keto diet or intermittent fasting plan.
While following a keto diet, it’s important to be mindful of your alcohol consumption, as some alcoholic beverages can be high in carbohydrates and potentially disrupt ketosis.
However, there are keto-friendly options available for those who wish to enjoy an occasional drink. Keep in mind that moderation is key, and alcohol should always be consumed responsibly.
Dry wines, both red and white, are generally low in carbohydrates and can be enjoyed in moderation on a keto diet. Look for wines with lower sugar content, such as:
A standard 5-ounce serving of dry wine typically contains 3-4 grams of carbohydrates.
Brut, Extra Brut, or Brut Nature Champagne and sparkling wines are also low in carbohydrates, making them suitable for a keto diet.
These options usually have less residual sugar compared to sweeter sparkling wines. A standard 5-ounce serving of Brut Champagne contains approximately 2-3 grams of carbohydrates.
Unflavored spirits such as vodka, gin, whiskey, rum, and tequila are virtually carb-free and can be enjoyed on a keto diet.
However, be cautious of flavored spirits, as they may contain added sugar or carbohydrates. When consuming spirits, opt for calorie-free mixers like club soda, diet tonic water, or sparkling water. Adding a splash of lemon or lime juice can also enhance the flavor without adding significant carbs.
While traditional beers can be high in carbohydrates, there are low-carb beer options available. Light beers or beers specifically marketed as low-carb typically contain fewer carbs than their regular counterparts.
Some examples of low-carb beers include:
Hard seltzers have become increasingly popular in recent years and are generally low in carbohydrates. These drinks are made with sparkling water, alcohol, and natural flavors.
Some keto-friendly hard seltzers include:
Remember to drink alcohol in moderation and be aware of its potential impact on your weight loss goals and overall health. Consuming too much alcohol can slow down weight loss and lead to other health issues.
If you choose to drink alcohol while following a keto diet, opt for these keto-friendly options and be mindful of portion sizes.
Navigating parties and social events can be challenging when following a keto diet. However, with some planning and strategic choices, you can still enjoy yourself without compromising your dietary goals.
Here are some tips to help you stay on track at parties and social events:
By following these tips, you can successfully navigate parties and social events while maintaining your keto lifestyle.
Remember to stay focused on your goals and enjoy the company of others, making the event a positive experience that supports your health and well-being.
Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for individuals with diabetes, especially when adopting a new diet like the ketogenic diet. Blood sugar monitoring can help you:
When starting a ketogenic diet, it’s essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to adjust your medications as needed. As the keto diet can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels, you may require changes in your medication regimen. Here are some factors to consider:
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, is a potential concern for individuals with diabetes, especially when starting a new diet like the keto diet. It’s essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and know how to manage it. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include:
If you suspect hypoglycemia, take the following steps:
By recognizing and managing hypoglycemia effectively, you can maintain better blood sugar control and avoid potential complications related to low blood sugar levels.
This comprehensive guide has provided valuable information for individuals with diabetes looking to adopt a ketogenic diet and intermittent fasting routine while maintaining their blood sugar levels. By understanding the principles of the keto diet, its benefits for diabetics, and how to start, individuals can make informed decisions about their dietary choices.
With a wide range of keto-friendly alternatives to favorite foods, snacks, and beverages, adhering to a low-carb lifestyle can be both enjoyable and sustainable.
Additionally, intermittent fasting, when done correctly and in consultation with healthcare professionals, can offer additional health benefits for diabetics. Navigating restaurant menus, attending parties, and social events are also possible with a little preparation and knowledge of keto-friendly options.
Monitoring and managing blood sugar levels remain essential for diabetics, regardless of their chosen dietary approach. Adjusting medications, recognizing hypoglycemia, and maintaining regular communication with healthcare providers are vital components of successful diabetes management.
Remember, always consult with your healthcare provider before making significant changes to your diet or lifestyle, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or concerns.
By taking a proactive approach to diabetes management and incorporating the strategies discussed in this guide, individuals can enjoy a variety of delicious foods, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and optimize their blood sugar control.
By following this comprehensive guide, you’ll be well-equipped to manage your diabetes with a keto diet and intermittent fasting. With delicious keto-friendly alternatives to your favorite foods and treats, you can enjoy a satisfying and healthy lifestyle while better managing your diabetes.
In stock | Free shipping
In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products/services are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.

If you’re looking for a comprehensive, natural solution to tackle inflammation and its debilitating effects, you’re in the right place. Welcome to the new era

The Invisible Enemy Within You wake up feeling groggy, your joints ache, and that old neck pain seems to have returned. No, it’s not just

CBG oil has been creating waves in the health and wellness industry, and for good reasons. But with any health trend, it’s crucial to separate

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping
In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

FREE SHIPPING & DELIVERY INSURANCE
Enjoy free ground shipping and free delivery insurance on all orders! Spend $150+ to unlock free 2-Day Air shipping.

24/7 EXPERT SUPPORT
Text (323) 352-9131 anytime for help from one of our USA Medical experts. We’re here for you!

Get your first-time coupon!
This coupon has no restrictions on your first purchase, you can use it for anything at USA Medical!

Join the USA Medical Family!
Get access to exclusive offers and free giveaways in our private Facebook group.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. USA Medical products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any diseases. Individual results may vary.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy & Terms of Service apply.
© USA Medical, 2025. All rights reserved.

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping