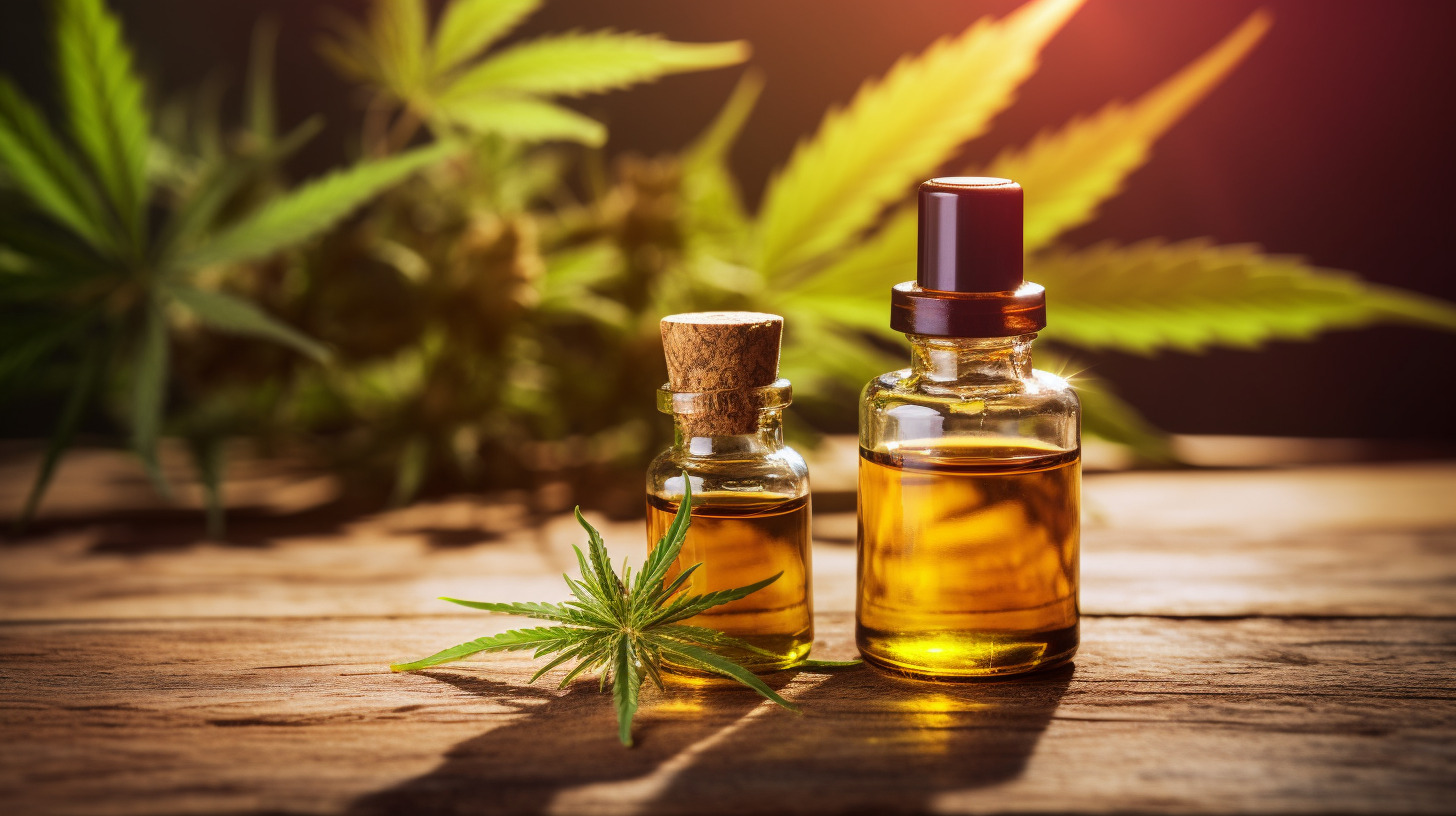

What Is CBG Oil?
If you’re looking for a comprehensive, natural solution to tackle inflammation and its debilitating effects, you’re in the right place. Welcome to the new era

Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in the body, participating in over 300 enzymatic reactions. While it can be found in a variety of foods, many people do not get enough of this mineral in their diet. Magnesium glycinate is a highly bioavailable form of magnesium that can be taken as a dietary supplement to improve magnesium levels. This article will cover some of the positive side effects of magnesium glycinate.
One of the primary benefits of magnesium glycinate is its ability to reduce muscle cramps and spasms. This is because magnesium is involved in muscle contractions and relaxation. Adequate magnesium intake can help prevent muscle spasms and cramps, making it particularly useful for athletes and people with physically demanding jobs.
In addition to its muscle-relaxing effects, magnesium glycinate can also improve sleep quality. This is because magnesium helps regulate the production of melatonin, a hormone that plays a central role in sleep. Increasing magnesium intake may make it possible to fall asleep faster and sleep more soundly.
Magnesium glycinate can also have a positive effect on mental health. It has been shown to reduce anxiety and stress, potentially by regulating the production of stress hormones such as cortisol. Magnesium glycinate may also help lower blood pressure, as magnesium regulates blood vessel constriction and relaxation.
Magnesium is also important for bone health. It helps regulate calcium levels in the body, which is crucial for maintaining strong bones. Some studies have suggested that magnesium glycinate may help improve bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Furthermore, magnesium glycinate may improve insulin sensitivity and help manage diabetes. It is thought that magnesium helps regulate blood sugar levels and may improve the body’s ability to use insulin, the hormone that helps transport sugar from the blood into cells.
Magnesium glycinate is considered to be a more bioavailable form of magnesium compared to other forms, such as magnesium oxide or magnesium citrate. This means that it is more easily absorbed and utilized by the body. It is also less likely to cause digestive side effects, such as diarrhea, that can be common with other forms of magnesium.
If you are interested in incorporating magnesium glycinate into your routine, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional first. The recommended daily magnesium intake varies depending on age and gender, but the National Institutes of Health recommends a daily intake of 310-420 mg for adult men and women, respectively.
There are many foods that are high in magnesium, including leafy green vegetables, nuts and seeds, and whole grains. In addition to dietary sources, magnesium glycinate is also available in supplement form. It is important to follow the dosage instructions on the supplement label and not to exceed the recommended daily intake.
Magnesium glycinate is a highly bioavailable form of magnesium that offers a variety of positive effects on the body, including reducing muscle cramps and spasms, improving sleep quality, reducing anxiety and stress, potentially lowering blood pressure, and improving bone health and insulin sensitivity. As with any supplement, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional before starting a new regimen.
Works Cited
“Magnesium: Possible Side Effects.” Mayo Clinic, https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-magnesium/art-20365095.
“Magnesium Supplements: What to Know Before You Buy.” Harvard Health Publishing, https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/magnesium-supplements-what-to-know-before-you-buy.
“Magnesium: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Dosage, and Warning.” WebMD, https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-998/magnesium.
“Magnesium Supplements: Benefits, Side Effects, Dosages, and More.” Healthline, https://www.healthline.com/health/magnesium-supplements.
“Magnesium Glycinate: Uses, Dosage, and Side Effects.” Medical News Today, https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/324048
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products/services are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.

If you’re looking for a comprehensive, natural solution to tackle inflammation and its debilitating effects, you’re in the right place. Welcome to the new era
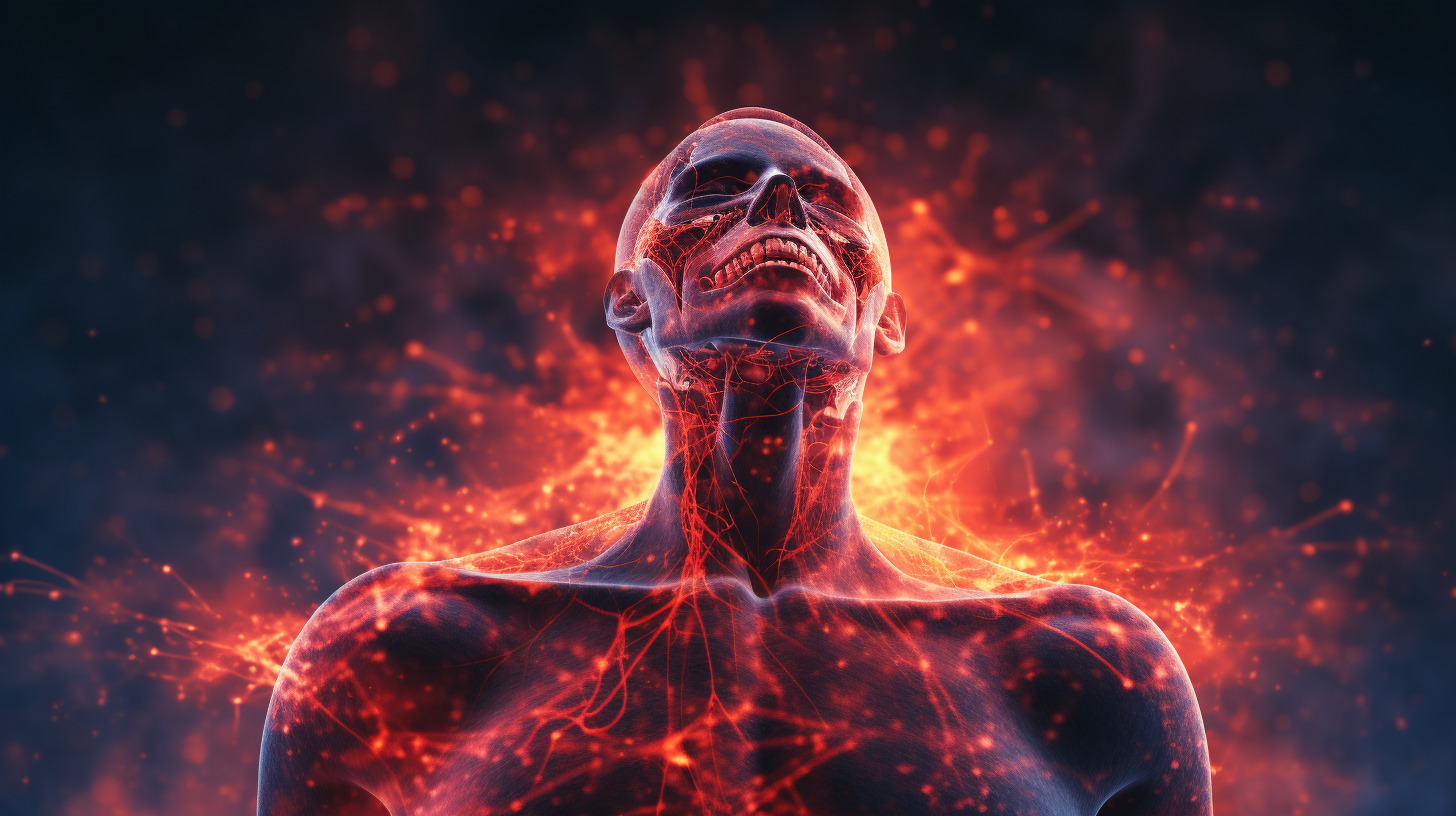

The Invisible Enemy Within You wake up feeling groggy, your joints ache, and that old neck pain seems to have returned. No, it’s not just
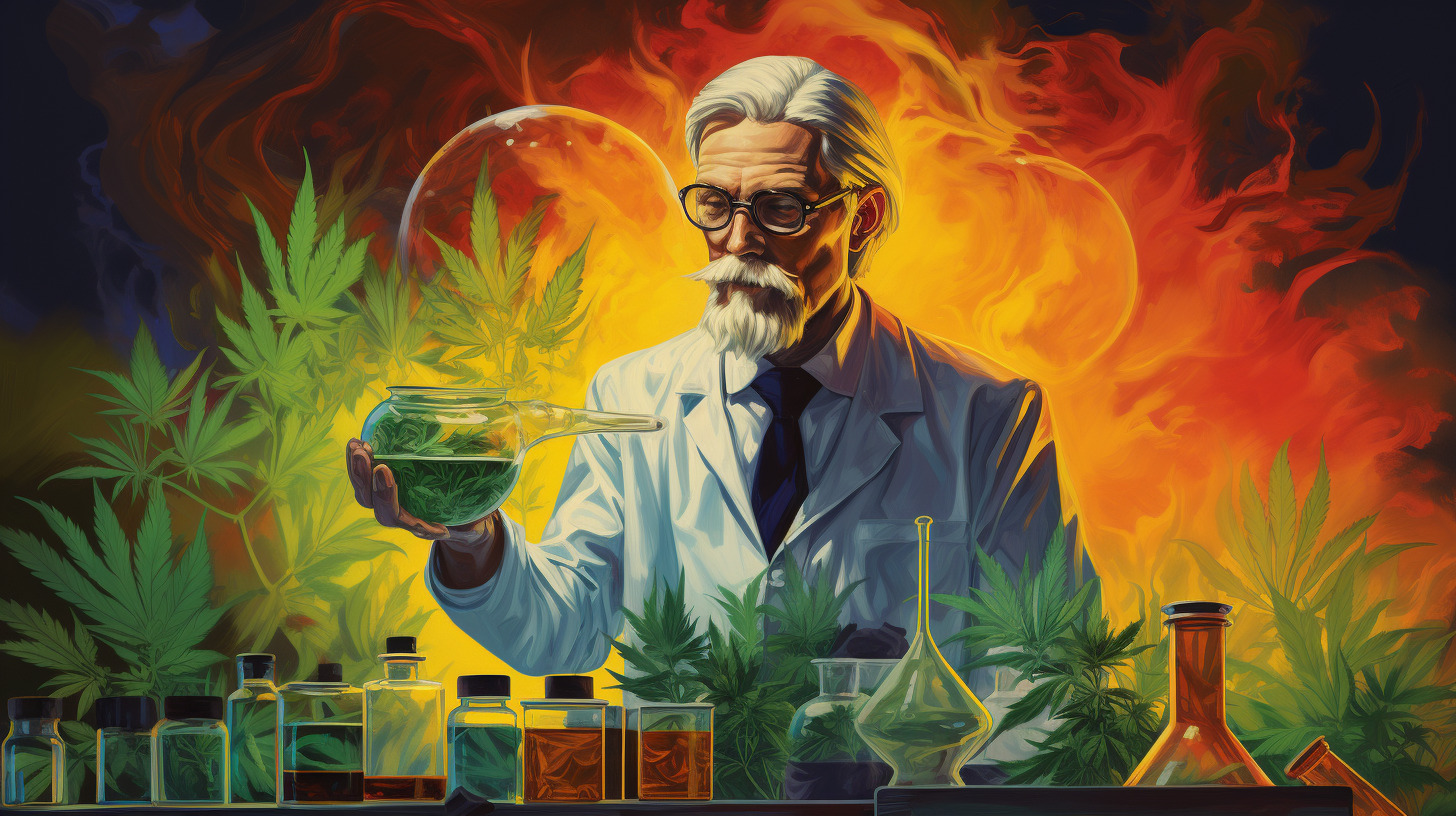

CBG oil has been creating waves in the health and wellness industry, and for good reasons. But with any health trend, it’s crucial to separate

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping
In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping
In stock | Free shipping
In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping