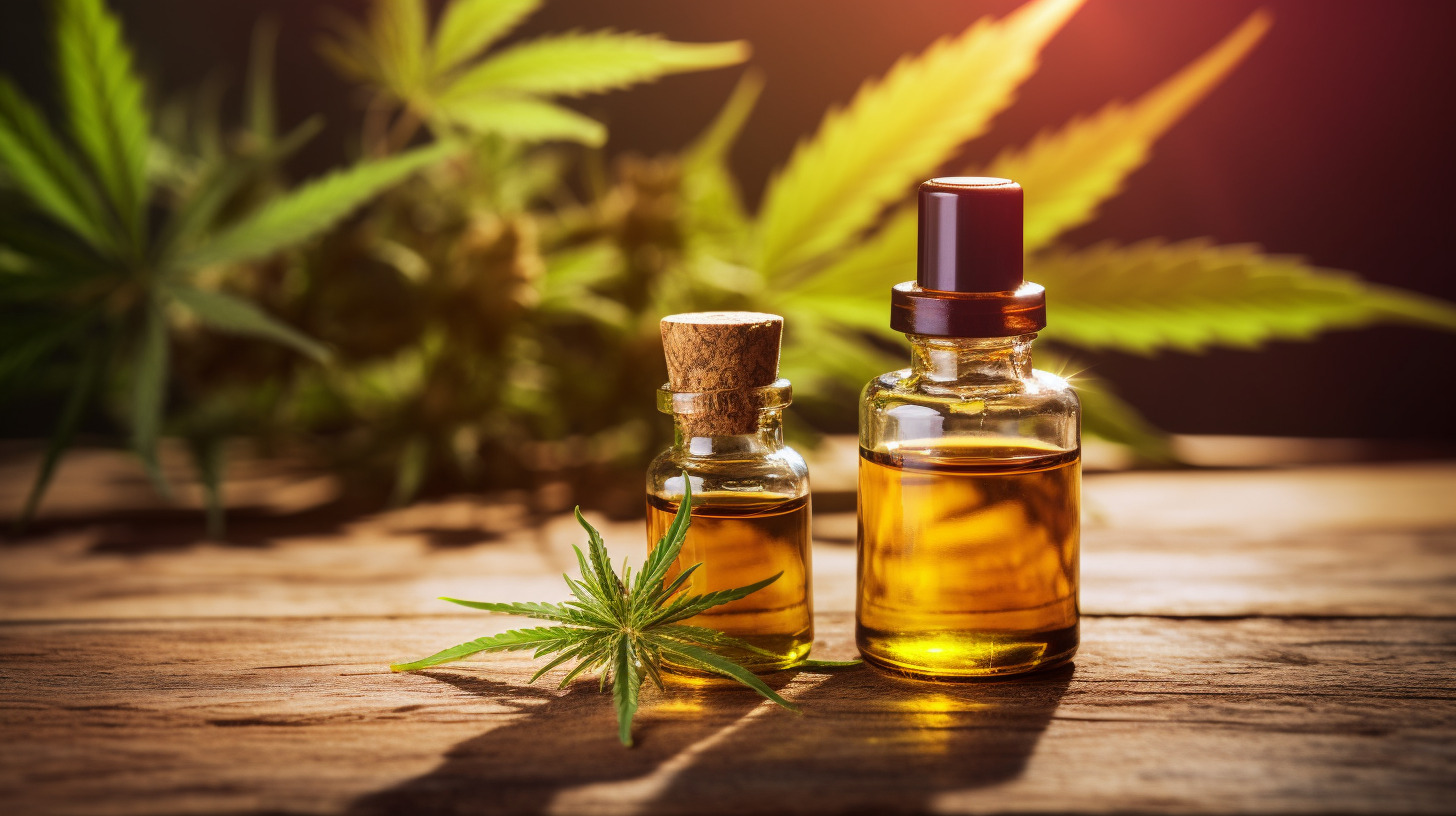

What Is CBG Oil?
If you’re looking for a comprehensive, natural solution to tackle inflammation and its debilitating effects, you’re in the right place. Welcome to the new era

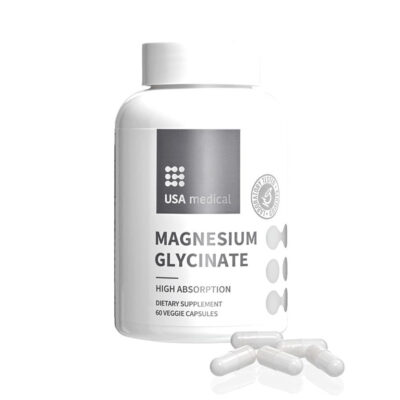
Magnesium glycinate is a form of essential magnesium bound to glycine, an amino acid in our bodies. It is known for its high bioavailability, meaning that it is easily absorbed by the body, making it a popular choice for people looking to supplement their magnesium intake as well as those who want to take magnesium glycinate for sleep!
One of the primary positive benefits of magnesium glycinate is its ability to improve sleep quality. Magnesium plays a vital role in the body’s sleep-wake cycle by regulating the production of melatonin and supporting muscle relaxation. When the body is deficient in magnesium, it can lead to restlessness, difficulty falling asleep, and wakefulness during the night.
In one study, elderly participants with insomnia were given a daily dose of magnesium glycinate for eight weeks. The results showed that the supplement significantly improved sleep quality and duration and reduced the time it took to fall asleep.
Another study looked at the effects of magnesium glycinate on people with sleep disorders caused by alcohol withdrawal. The results showed that the supplement significantly improved sleep efficiency and reduced the number of awakenings during the night.
Magnesium glycinate may also reduce the severity of sleep disorders such as restless leg syndrome (RLS). RLS is a condition characterized by an overwhelming urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. It can cause difficulty falling asleep and interrupt sleep during the night. In a study of participants with RLS, magnesium glycinate supplements were found to reduce the severity of symptoms and improve sleep quality.
In addition to its sleep-promoting effects, magnesium glycinate has a number of other potential health benefits. It has been shown to reduce muscle cramps and spasms, lower blood pressure, and improve insulin sensitivity, making it beneficial for people with diabetes. It may also help with anxiety and stress by supporting the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a role in mood regulation.
While it is possible to get sufficient magnesium through diet alone, many people may not get enough of the mineral through what they eat. Foods rich in magnesium include leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. However, if you cannot meet your magnesium needs through diet alone or have a medical condition requiring an increased mineral intake, supplementation with magnesium glycinate may be an option.
It is important to speak with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen; however, for most people, magnesium glycinate is a safe and effective way to increase magnesium intake and improve sleep quality.
Magnesium glycinate is a form of magnesium that is easily absorbed by the body and has been shown to have a number of positive benefits for sleep quality. It may improve sleep efficiency and duration, reduce the severity of sleep disorders such as restless leg syndrome, and support the production of the sleep hormone melatonin. In addition to its sleep-promoting effects, magnesium glycinate may also have other potential health benefits such as reducing muscle cramps and spasms, lowering blood pressure, and improving insulin sensitivity. While it is possible to get sufficient magnesium through diet, supplementation with magnesium glycinate may be an option for those unable to meet their needs through diet alone or have a medical condition requiring an increased mineral intake. As with any supplement, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider before starting a magnesium glycinate regimen.
Works Cited
“The role of magnesium in sleep: An update and recommendations” by D. D. Dominguez and D. J. Boulet, Sleep Medicine Reviews, vol. 33, 2016, pp. 37-43. This review article provides an overview of the current understanding of the role of magnesium in sleep, including its impact on insomnia, sleep quality, and sleep architecture.
“Magnesium supplements for primary insomnia: a systematic review” by J. J. Afaghi and P. O’Connor, Journal of Sleep Research, vol. 20, no. 2, 2011, pp. 207-213. This systematic review summarizes the existing research on the use of magnesium supplements as a treatment for primary insomnia.
“Magnesium and sleep” by E. Levandovski, et al., Sleep Medicine Reviews, vol. 16, 2012, pp. 367–372. This review article discuses the potential mechanism of magnesium on sleep regulation, showing its effects on neurotransmitters and sleep-related hormones.
“Magnesium glycinate improves sleep quality in insomnia patients: a randomized clinical trial” by S. A. Akhondzadeh, et al., Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, vol. 15, no. 10, 2010, pp. 825-829. This randomized clinical trial assess the effects of magnesium glycinate on sleep quality in patients with insomnia.
“The Effects of Magnesium Supplementation on Subjective Measures of Insomnia in Adult Populations: A Meta-Analysis” by J. J. R. Est Eid, et al., Journal of Sleep Research, vol. 26, no. 6, 2017, pp. 675-684. This meta-analysis assesses the effect of magnesium supplementation on subjective measures of insomnia in adult populations.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products/services are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.

If you’re looking for a comprehensive, natural solution to tackle inflammation and its debilitating effects, you’re in the right place. Welcome to the new era
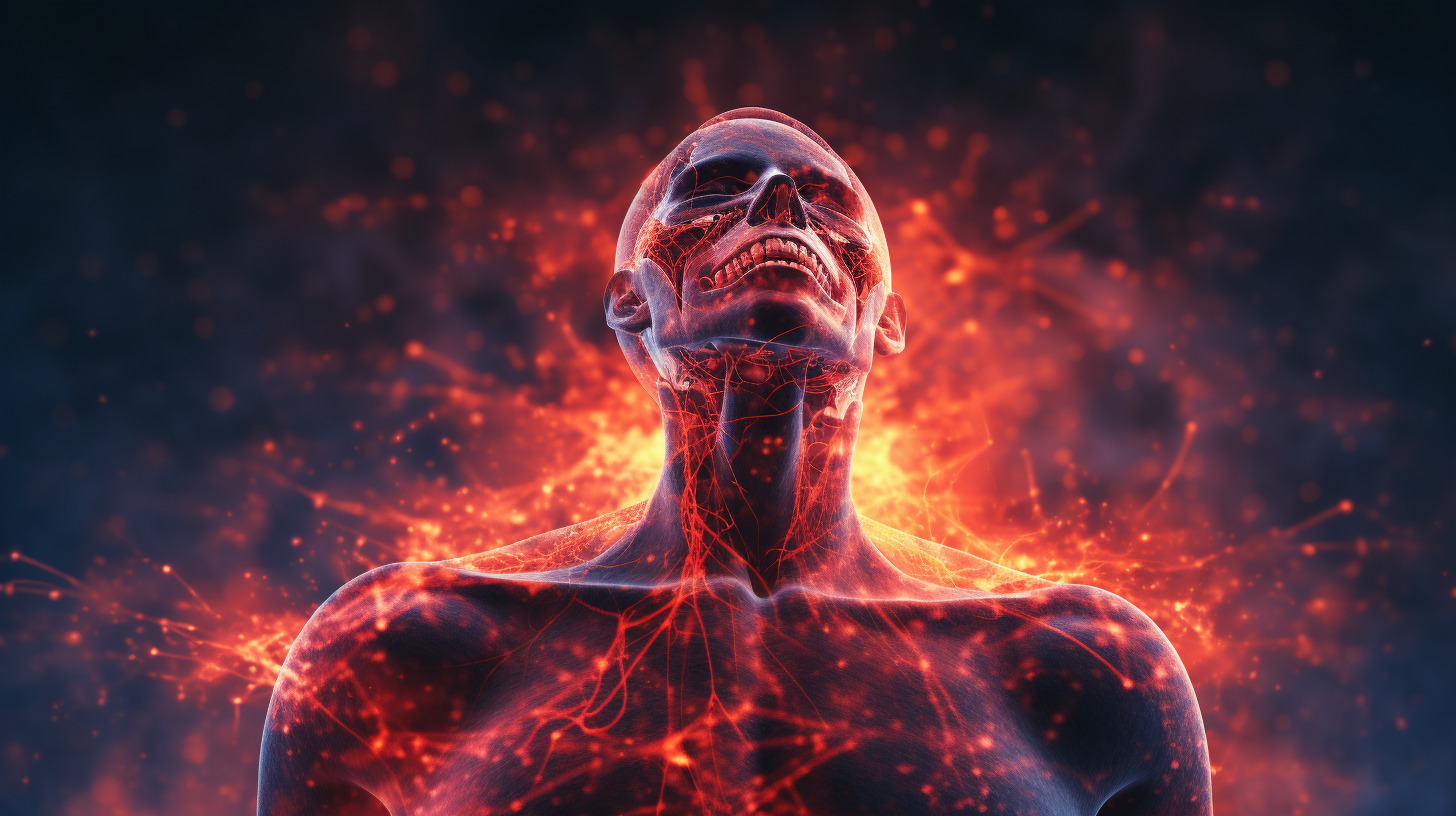

The Invisible Enemy Within You wake up feeling groggy, your joints ache, and that old neck pain seems to have returned. No, it’s not just
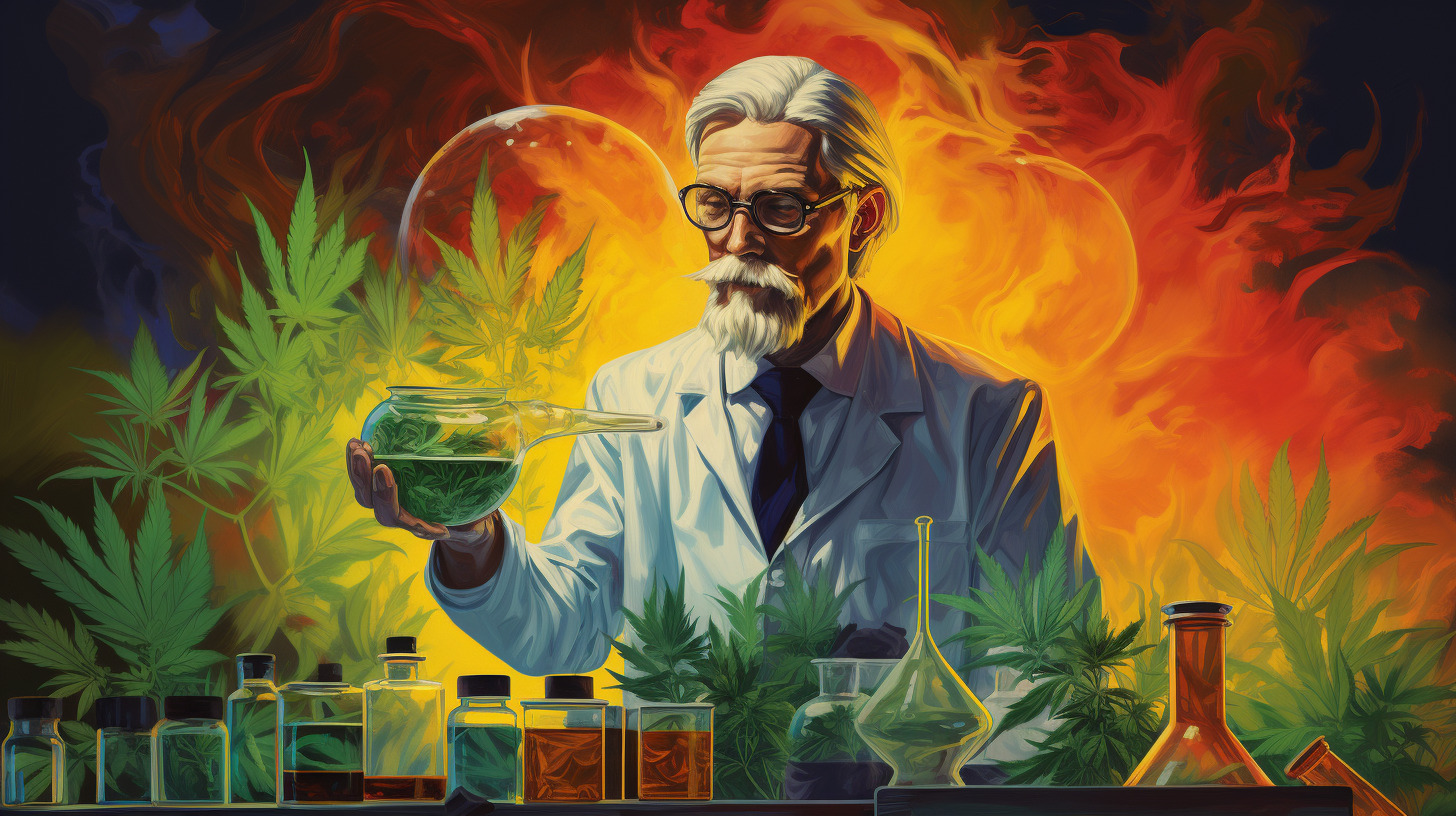

CBG oil has been creating waves in the health and wellness industry, and for good reasons. But with any health trend, it’s crucial to separate

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping
In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping
In stock | Free shipping
In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping

In stock | Free shipping